————————-
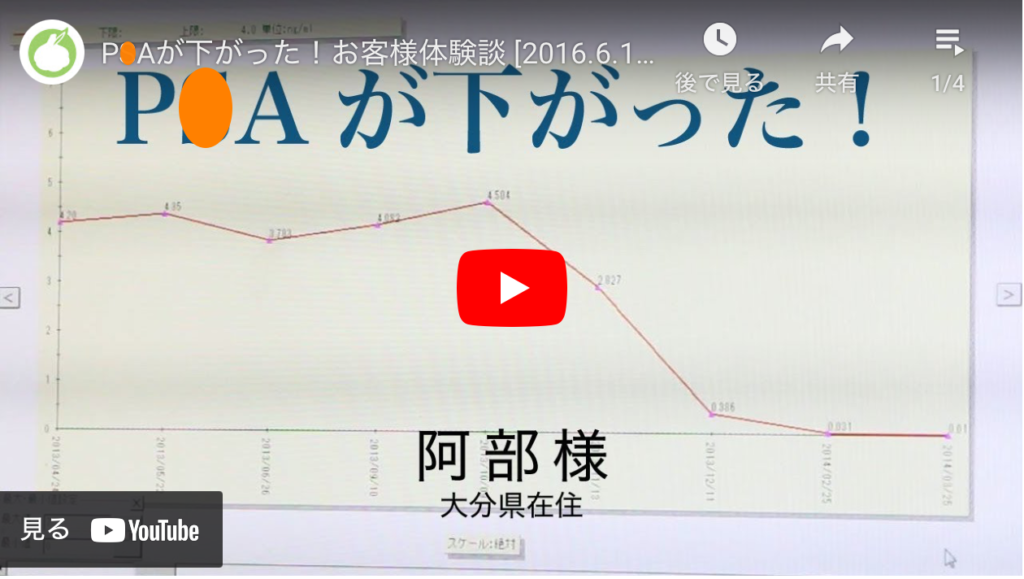
PSAが4.0だったところ、病院に通いながら、にんにくスプラウトパウダーの健康食品も飲用して4、5ヶ月になります。現在は、0.0##(検索広告掲載ガイドラインに準拠するため数値を表示しておりません)になりました。
私の様子をみて妻も一緒に飲むようになりました。
ありがとうございました。
(2023年6月17日)
【お願い】当サイトでご紹介しているお客様の声は、実際のご愛用者からお寄せいただいた感想を記載しています。あくまでも個人の主観による感想で効能や効果ではありません。予め、ご了承のうえご覧ください。
————————-
投稿者について:
都道府県: 大分県
性別: 男性
年齢: 70歳代
お名前(仮名): A 様
この体験談をいただくまでご愛飲箱数: 5箱